
by Jean Marie Carey | 12 Feb 2016 | Animals, Animals in Art, Art History, Franz Marc

Franz Marc, Zwei Katzen, blau und gelb, 1912
The College Art Association conference was held 3-6 February in Washington, D.C., which for what I study is not a very interesting art city in the way New York City is…and D.C. is thus also very expensive to visit, since the trip doesn’t include a few precious hours in the Met, MoMA, Guggenheim, Neue Galerie, and so on.
If conferencing, not museum-visiting, is to be CAA’s focus going forward, the organization should do what the German Studies Association does, and move the meeting to some less-costly destinations that still have good mass transit and more of a range of hotel rooms, like Las Vegas or Atlanta.
This conference I had a lot of tasks I actually had to do, and one I wanted to do, or I should say was very curious about doing, attending the Historians of German, Scandinavian and Central European Art, or HGSCEA, [formerly just HGCEA, but, I guess the Munch people or something…] meeting, which this year took the form of a dinner honoring the long-reigning and undisputed chief Kandinsky scholar, Rose Carol Washton Long of the Graduate Center of the City University of New York, and Charles Haxthausen from Williams College.
I took the cryptic “honoring” on the invitation to mean “retiring,” which put me in mind of The King of the Cats. Miss Jessel’s “Haunted Palace” blog gives a nice account of the oral history tradition of this tale and its place in the folklore of the British Isles but, basically, without belaboring the point the outstanding extra-narrative moral for cat lovers and observers is probably that upon learning of the death of “the king of the cats,” all cats think that they are the designated heir to the throne.
So with respect to the fractious group of people who comprise known Kandinsky scholars…without an obvious heir apparent (to my mind there is not one, the once-promising regent having chosen their battles poorly), wouldn’t they all be prepared for anointment? As it turned out RCWL, in her very congenial speech, immediately made clear that while she was retiring from CUNY, she would not be relinquishing the reins to the Kandinsky dynasty anytime soon.
 The “party” itself was quite a mysterious affair in that it did not appear as an “affiliated society” event anywhere on the CAA schedule (or the new Linked-In developer-sponsored) app, and was held in a small restaurant in Adams Morgan which was entirely closed except for the HSGCEA dinner. RSVP, affiliation, and credentials were thoroughly vetted at the door, and there were no nametags. Nametags would not have been much use anyway, since everyone went by a non-apparent nickname, like “Ricki” or “Mark.” And it was very dark inside the restaurant, Lillie’s (actual lighting shown), and you couldn’t see even across the room. So in other words it was pretty much how I expected it to be, except there wasn’t any kind of St. Bartholomew’s day type of fracas, duel, or mass feline exit through the fireplace.
The “party” itself was quite a mysterious affair in that it did not appear as an “affiliated society” event anywhere on the CAA schedule (or the new Linked-In developer-sponsored) app, and was held in a small restaurant in Adams Morgan which was entirely closed except for the HSGCEA dinner. RSVP, affiliation, and credentials were thoroughly vetted at the door, and there were no nametags. Nametags would not have been much use anyway, since everyone went by a non-apparent nickname, like “Ricki” or “Mark.” And it was very dark inside the restaurant, Lillie’s (actual lighting shown), and you couldn’t see even across the room. So in other words it was pretty much how I expected it to be, except there wasn’t any kind of St. Bartholomew’s day type of fracas, duel, or mass feline exit through the fireplace.
As to my own paper and panel, I was thrown off my presentating game a little – not a lot, or not as much as I had expected or was undoubtedly intended – and got a lot of good questions, including some very specific queries from some more-than-casual idolators about Animalisierung, of all things, about the painting Tierschicksale, and about what I had specifically set out to talk about, affect/effect disturbing/calming animal images have upon human animal/human-animal empathy.
Basically my claim is that disapprobation toward animal abusers – such as generated by the film The Cove and the work of Sue Coe – is not as strong a motivator as true identification with the animal subject. Hence the focus on Franz Marc. This isn’t necessarily as obvious an idea as it seems, and bears more discussion and exploration (which is why I am writing about it).

by Jean Marie Carey | 11 Jan 2016 | Animals, Animals in Art, Art History, Dogs!, Expressionismus, Franz Marc, German Expressionism / Modernism
In the spirit of rebirth an excerpt from my research about Franz Marc’s visualization of a kind of pantheistic utopia, followed by an introduction and explanation about this new website and some other breaking German Modernism news.
§ § §
Though it doesn’t seem as if these two images appended here could possibly be related, they do have a commonality – the figures are in a state of private reverie that is between sleep and wakefulness.

Franz Marc, Der Traum, 1912.
Franz Marc himself charaterized his mode of trying to perceive as the animal as if in a state of somnambulism, partly conscious yet also given over to the transformative experience of being another, in this dream-like state. The animals to Marc possessed in their purity a sort of natural extraconsciousness. His work has numerous examples of figures in such a “sleepwalking” state, corresponding to the posture of animals, and also people, in a relaxed posture reclining into a receptive earth. This natural somnambulism blurred what was conventionally taken to be a distinction between people and animals, that animals are innate and instinctive, whereas humans can return to this state only in dreams.
In 1911, Marc had written an interesting personal aside in his journal:
[Können wir uns ein Bild machen, wie wohl Tiere uns und die Natur sehen?]
Gibt es für Künstler eine geheimnisvollere Idee als die [Vorstellung], wie sich wohl die Natur in dem Auge eines Tieres spiegelt? Wie sieht ein Pferd die Welt oder ein Adler, ein Reh oder ein Hund? Wie armselig, [ja] seelenlos ist unsre [Gewohnheit] Konvention, Tiere in eine Landschaft zu setzen, die unsren Augen zugehört statt uns in die Seele des Tieres zu versenken, [daß wir das seinen Blick Weltbild] um dessen Bilderkreis zu erraten.
[Diese Betrachtung soll keine müßige causerie sein, sondern uns zu den Quellen der Kunst führen.]1
We can see this interest in the perception of animals reflected not just in Marc’s belief in the inherent Beseeltheit [2] of animals but also in his knowledge of contemporary zoology research taking place at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries, for example, the writings of Wilhelm Bölsche on plant and animal taxonomy[3] and more clinical examinations, such as studies about how the retinae of insects’ eyes functioned.[4]
Thus what we think of now as “the question of the animal” was under Marc’s consideration in suprisingly contemporary terms, and should not be considered merely an outflow of his private, sentimental feelings about his pets. Like Kandinsky, Marc was curious as to whether there was a tangible basis for their claims that there existed unseen dimension in the regular order of the world but which had become invisible to callous, spiritually deprived humans.
The sketch, Liegender Hund (Russi), (and note also the title) shows that even before he began to wrangle with the problem of color, Marc was busy practicing making copies and models for his later paintings, sketches which nonetheless stood as discrete works for Marc, since, in his somewhat haphazard fashion, he also named and numbered them.
Unlike Paul Gauguin, from whom he certainly drew upon for ideas about content and color, to Marc, nude women in a natural setting were not excuses for a prurient gaze but rather these women, like Marc’s contemplative animals, symbolized innocence and purity, and were associated with the reclamation of paradise. Dreaming animals and people stood for a somnambulant state marking a kind of emotional perception that synaesthetically included auratic impressions and warmth.[5] In his painting Der Traum in which a “Wilden” woman sits cross-legged. Marc blends this image of longing for an original paradise with the European idea of paradise, where the wild lion, like that of St. Jerome, lives in peaceful harmony with horses and humans. Marc’s Animalisierung is in evidence here. Like “wild” people, animals as envisaged by Marc display a natural attunement to the spheres, having been born directly into their instincts, which modern humans – expelled from paradise – have lost.
(more…)
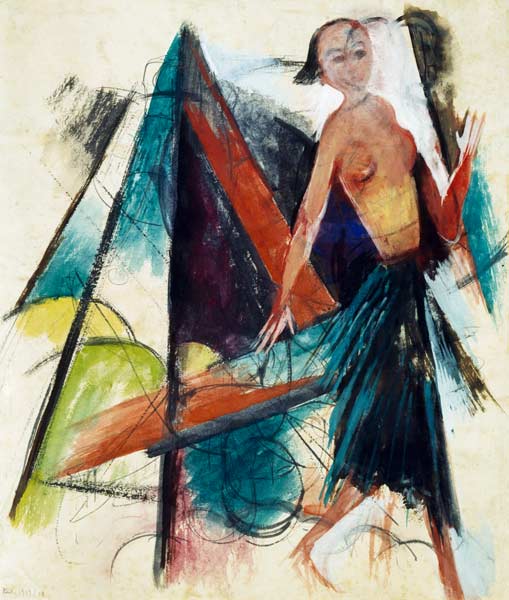

by Jean Marie Carey | 24 Nov 2015 | Art History, Expressionismus, Franz Marc, German Expressionism / Modernism, Re-Enactments© and MashUps

Miranda, 1914
So I am pleased and grateful to report the publication of my first peer-reviewed anthology chapter in the journal Expressionismus in the special issue Der performative Expressionismus. The article is called “‘Der Sturm’ und die Wilden.? Franz Marcs Entscheidungskampf mit der Theatralität,” which translates imperfectly to something like “‘The Tempest’ and the Savages: Franz Marc’s Decisive Encounter with Theatricality.” (Entscheidungskampf can also mean something like Armageddon/scorched earth, which in this case is accurate.)
The article is currently behind the Neofelis Verlag paywall (for a very reasonable €13), but you will soon find it on JSTOR and elsewhere. If you have any questions about how to view article please email me.
This side project to my main research corrects some chronological errors that have consistently been repeated in both Expressionist and Dada literature about the collaboration of Franz Marc and Hugo Ball on a planned production of The Tempest at the Münchner Kammerspiele. Because the story takes place in early 1914, it has been tempting for scholars – some of them quite formidable – to conclude that it was the war that usurped these plans. However, that is not at all the case.
“What really happened” is of course quite interesting on its face and as a reminder that we in fact know very little in the way of actual facts about the historical avant-gardes, who are fast disappearing into hagiography.
More interesting to me, in terms of writing and research, was the analysis of the two small drawings Marc made as character studies of The Tempest’s Miranda and Caliban personalities. This is the first time these drawings, housed in the Kunsthalle Basel, have been subjected to such scholarly scrutiny and each contains many clues and psychological implications.
I was also intrigued to discover that Marc had sent a draft of his June 1914 essay »Das abstrakte Theater,« (also analyzed in the article) about his frustrating foray into the theater to August Macke, and that the two had previously had many exchanges about the performing arts. In fact it is clear that the very precocious Macke – who at only 21 had been the chief set designer for the theater in Düsseldorf – had had a great influence on Marc’s ideas on the subject – ideas being the key word, since Marc had no firsthand dramaturgical knowledge up until this point.
My colleague here at the university, Prof. Dr. August Obermayer, was the very gracious translator but he also provided invaluable editing and advising, and the Neofelis editors were also a pleasure to learn from.
All in all a great experience and I hope readers will find the unraveling of Expressionist mysteries as fascinating as I do.

Caliban, 1914

by Jean Marie Carey | 29 Aug 2015 | Animals, Franz Marc, German Expressionism / Modernism
My 2012 M.A. thesis, Franz Marc as an Ethologist, is now part of the online collection of the open-access Social Science Research Network (SSRN). You can download it or look at the abstract here.
UPDATE: I just can’t with Elsevier’s involvement with SSRN. In addition to Elsevier being generally evil, not supporting open access, and ruining the Pergamon imprint, more than a year after acquiring SSRN, there is still no discrete art history rubric, or way for authors to track who is looking at their work. But mainly Elsevier is garbage.

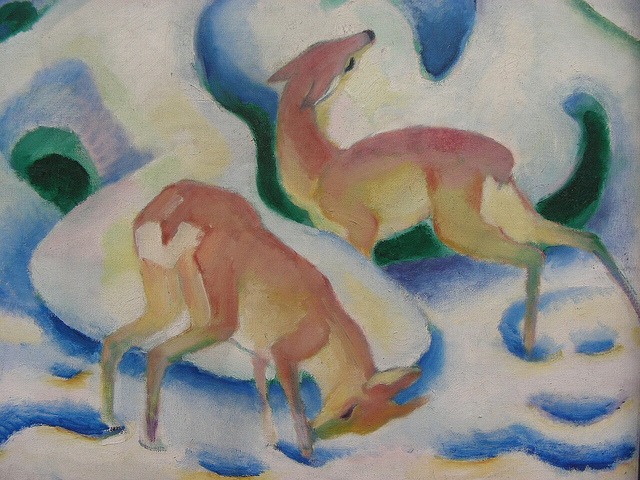
Franz Marc, Rehe im Schnee II, 1911, one of Marc’s paintings discussed in my thesis.
by Jean Marie Carey | 7 Jun 2015 | Animals in Art, Art History, Franz Marc

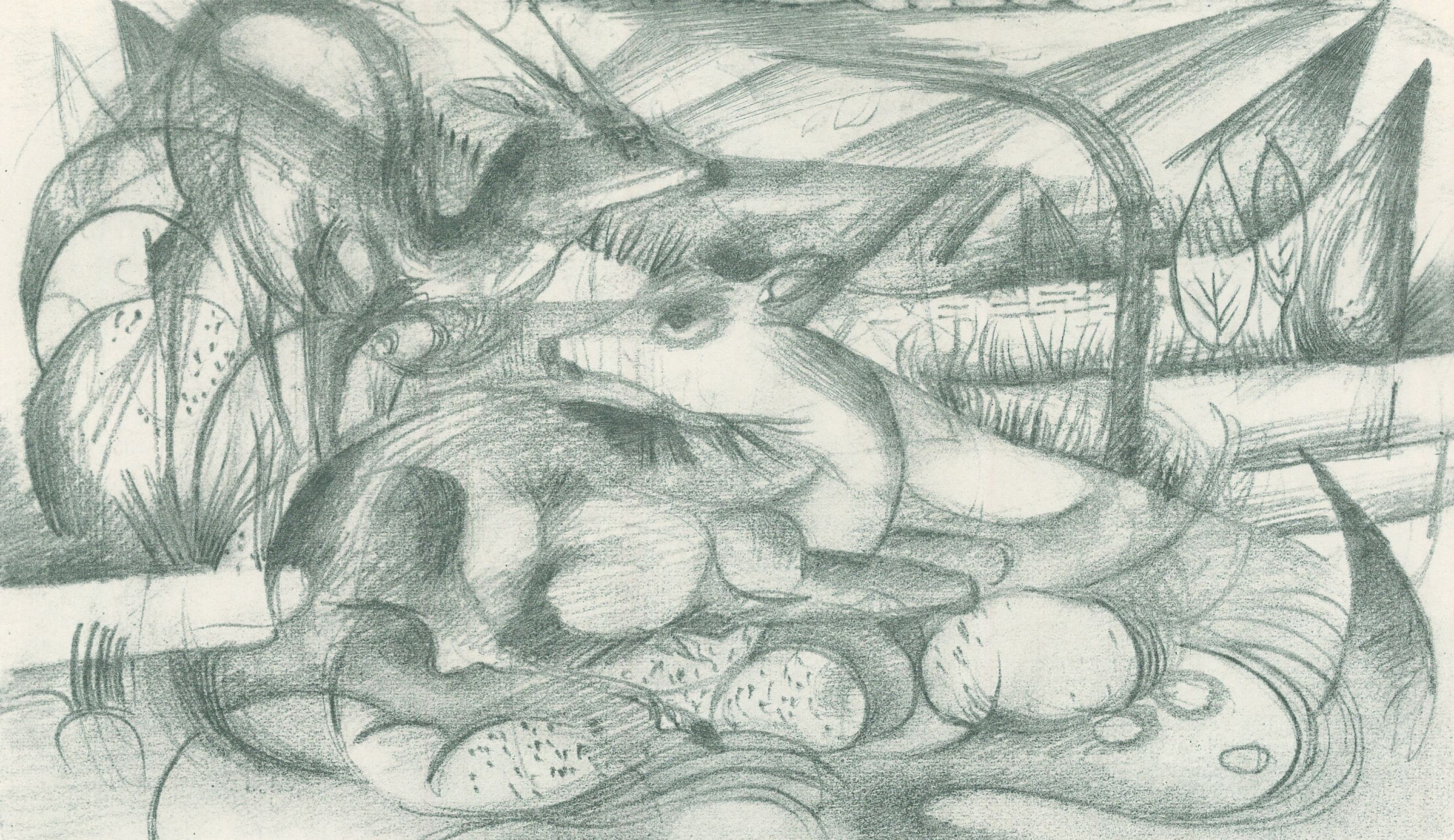
Franz Marc, Skizzenbuch aus dem Felde, Skizze 24, 1915
I recently looked harder at Franz Marc’s experiments with poetry. I think you could say that much of Marc’s writing borrows structurally from poetry, and Marc read a lot of poetry, including all of the classics you’d expect, work by people he actually knew, such as Gottfried Benn and Else Lasker-Schüler. He was also interested in French Symbolist Stéphane Mallarmé, particularly Un coup de dés jamais n’abolira le hasard of 1897, having extensively annotated a copy of the text; contact with Hugo Ball, who was influenced by Mallarmé’s text/design, probably heightened Marc’s attention.
From 1912 Marc made doodles of lines of the following poem here and there, and of course the last line is what Marc had originally intended to be the title of the painting we know as Tierschicksale (1914). But it was not until 1915 he wrote these phrases down all together in his small portfolio of drawings made in Germany and France, during the war. It’s hard to say what the poem means, especially in the context of the (approximately – some leaves may be lost) 35-page sketchbook’s compact animal images, it is very interesting. A translation is elsewhere but here is the original poem:
“…ein rosafarbner Regen viel [sic] / auf grüne Wiesen. / die Luft war wie grünes Glas. / das Mädchen [sah auf’s] blickte ins Wasser; das Wasser war klar [rein] wie Kristall; da weinte das Mädchen. / die Bäume zeigten ihre Ringe; die Tiere ihre Adern”.
(Abgedruckt in: Klaus Lankheit: Franz Marc: sein Leben und seine Kunst. Köln: DuMont 1976, S. 124.)

by Jean Marie Carey | 6 Apr 2015 | Animals, Animals in Art, Art History, August Macke, Dogs!, Expressionismus, Franz Marc, German Expressionism / Modernism, LÖL

Hund vor der Welt, Franz Marc (1912). Oil on canvas, 118 by 83 centimetres, private collection, Switzerland
I write about this painting a lot – in fact I once, for quite a long time, devoted my academic research solely to this painting – but I realised I don’t often say anything about it in this space. So here is a little excerpt not from my current chapters but from a side project.
§ § §
Franz Marc made an innovative painting – a metaphysical genre portrait of his dog Russi – called Hund vor der Welt in the spring of 1912. The large vertical canvas shows the white hound seated on a hillside, facing the sun and the landscape at an angle across an indeterminate space. We have an account of what Marc had in mind in making this image in particular and Marc’s other thoughts about painting his frequent model.[1] There is also a substantial amount of documentation about Russi, the dog, who, as the artist’s constant companion, was a character who populated the art, photographs, and writing of other people. We even know where Russi was born, how he came as a puppy to live with Marc, and when he died.[2] So despite its slightly whimsical affect, Hund vor der Welt is an image of a real dog about whom much historical information is available. Marc made many paintings in which Russi also appears as a peripheral regular “character;” he leads the way in Im Regen (1912) and leaps after Die gelbe Kuh (1911).
August Macke, who came into frequent contact with Russi and made his own drawings of the dog, prevailed upon Marc to change the name of the painting from the one Marc originally had in mind, So wird mein Hund die Welt sieht.3 We know from Marc that he wanted to show Russi in thought, so the dog’s seated posture suggests that this is what is happening in the stillness. The strange view of the landscape Russi “sees” is nonetheless completely identifiable as a typical one from around Sindelsdorf where Marc lived. By placing buildings in the recognizable, managed farmlands of Bavaria, Marc suggests that people and animals are part of the same ecology, which, for dogs as the primary animal of domestication, is certainly true.
Russi did not have the life of a working dog, instead, with Marc, dividing his time between Munich, Berlin, and the small towns of Sindelsdorf and Ried. Russi lost part of his tail in 1911, an adjustment to his appearance that is reflected in his 1912 portrait. This shows that Marc had a commitment to showing morphologically accurate details even about the animals he painted, even as the paintings themselves broke with academic naturalism.
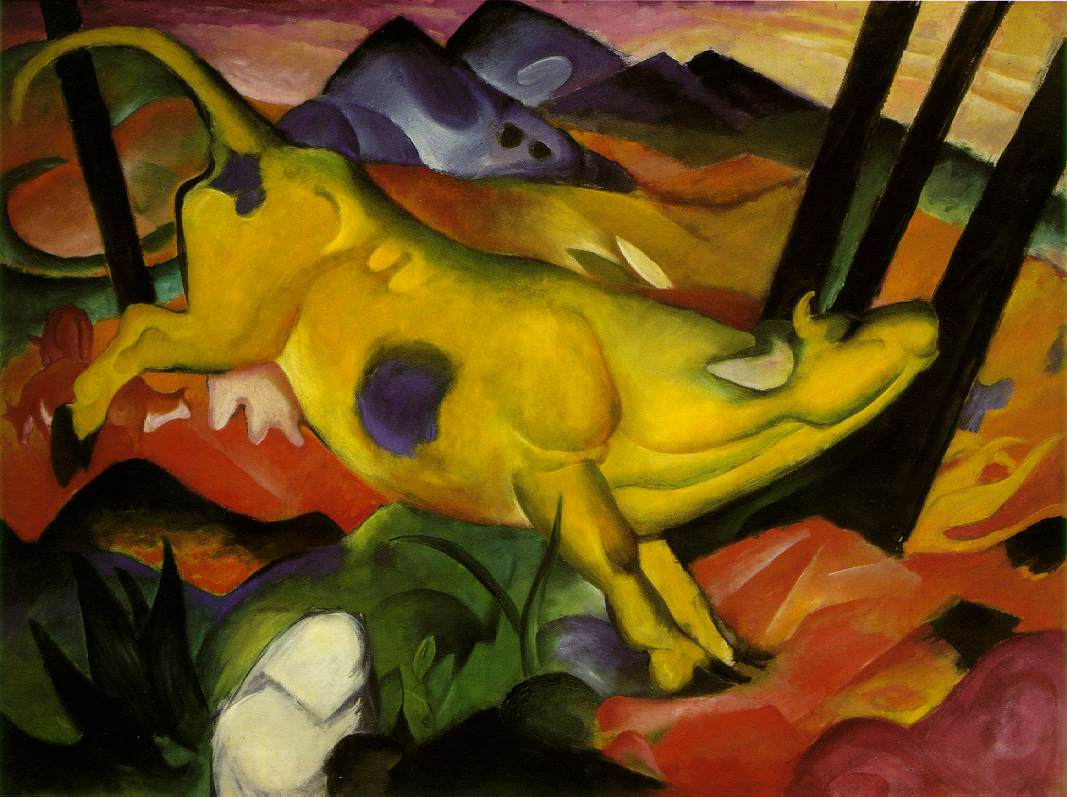

Die gelbe Kuh,
Franz Marc, 1911
189.2 × 140.52 cm
Oil on canvas
Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum, New York. That is Russi Marc in the lower left corner.
[1] Franz Marc, Briefe, Schriften und Aufzeichnungen, (Leipzig: Kiepenheuer, 1989), 11. Observing Russi at this moment, Marc wonders: “Ich möchte mal wissen, was jetzt in dem Hund vorgeht.”
[2] Marc, Briefe, 196-197.
[3] Franz Marc, August Macke, Briefwechsel, (Köln: DuMont, 1964), 124-126.

 The “party” itself was quite a mysterious affair in that it did not appear as an “affiliated society” event anywhere on the CAA schedule (or the new Linked-In developer-sponsored) app, and was held in a small restaurant in Adams Morgan which was entirely closed except for the HSGCEA dinner. RSVP, affiliation, and credentials were thoroughly vetted at the door, and there were no nametags. Nametags would not have been much use anyway, since everyone went by a non-apparent nickname, like “Ricki” or “Mark.” And it was very dark inside the restaurant, Lillie’s (actual lighting shown), and you couldn’t see even across the room. So in other words it was pretty much how I expected it to be, except there wasn’t any kind of St. Bartholomew’s day type of fracas, duel, or mass feline exit through the fireplace.
The “party” itself was quite a mysterious affair in that it did not appear as an “affiliated society” event anywhere on the CAA schedule (or the new Linked-In developer-sponsored) app, and was held in a small restaurant in Adams Morgan which was entirely closed except for the HSGCEA dinner. RSVP, affiliation, and credentials were thoroughly vetted at the door, and there were no nametags. Nametags would not have been much use anyway, since everyone went by a non-apparent nickname, like “Ricki” or “Mark.” And it was very dark inside the restaurant, Lillie’s (actual lighting shown), and you couldn’t see even across the room. So in other words it was pretty much how I expected it to be, except there wasn’t any kind of St. Bartholomew’s day type of fracas, duel, or mass feline exit through the fireplace.






 RSS - Posts
RSS - Posts